In the mining and construction industries, to make effective use of the rocks or ores obtained through quarrying or blasting, the materials need to be crushed to smaller sizes. This process is known as "size reduction" or "crushing". The purposes of crushing are as follows: obtaining the size or surface area required for the utilization of the ore or material, enabling easy transportation and storage, separating different minerals within the ore, and getting the size or surface area needed for the enrichment stage. Generally, the crushing process is divided into three stages:
1. PPrimary Crushing: The feed size ranging from 800 - 1500 mm is reduced to 150 - 300 mm. At this stage, large - scale rocks are initially broken down into more manageable sizes, which is a crucial step for further processing.
2. Secondary Crushing: The feed size of 150 - 300 mm from the primary crushing is further reduced to 50 - 80 mm. This stage refines the materials obtained from the primary crushing, making them suitable for the next - level processing requirements.
3. Tertiary Crushing: The size of 50 - 80 mm from the secondary crushing is decreased to 5 - 12 mm. In this final stage, the materials are crushed to the desired final sizes for various applications. The machine that performs the crushing process is called a crusher.
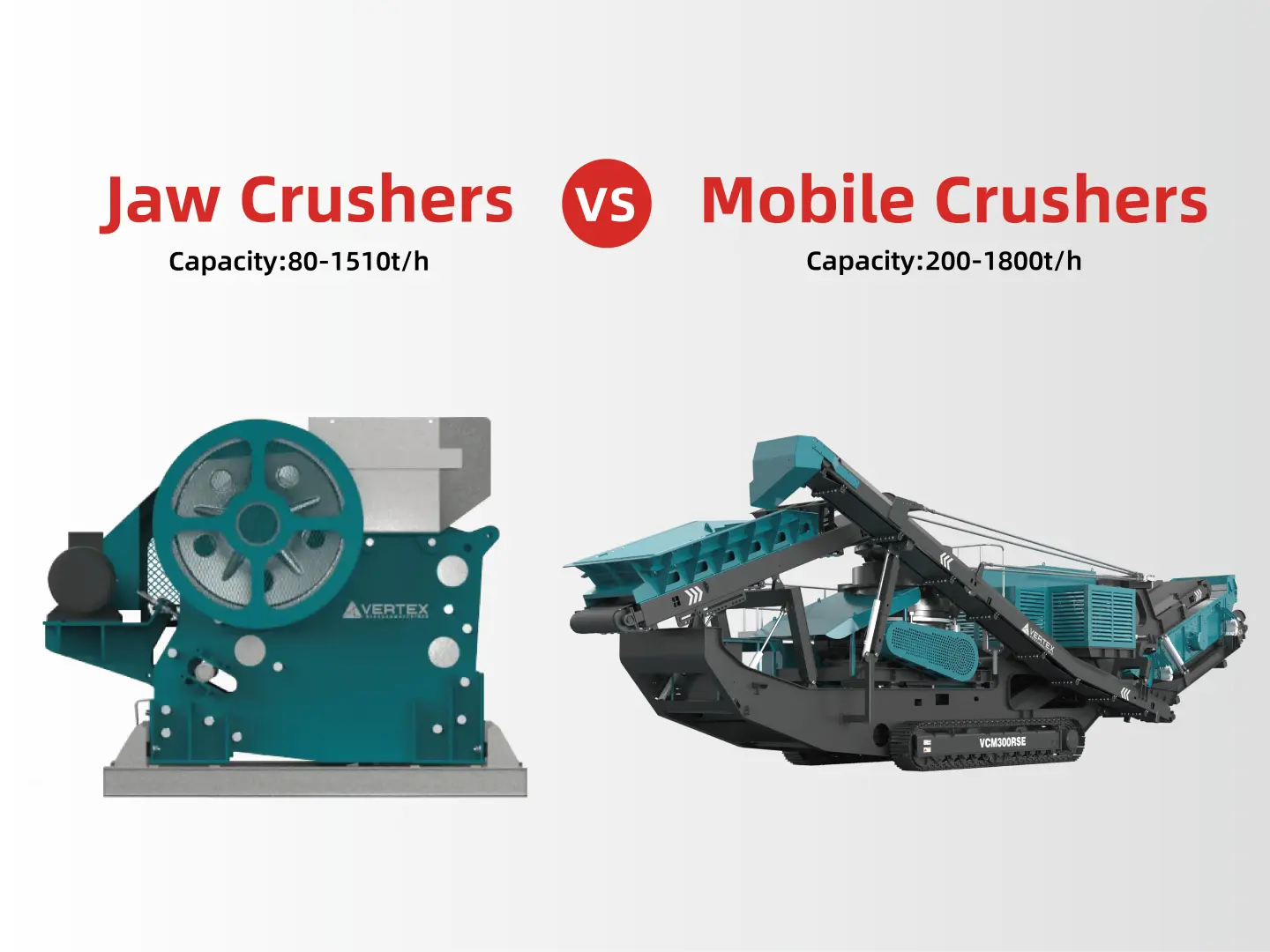
A jaw crusher is a type of crusher that is extensively used in the primary and secondary crushing processes. It is especially suitable for crushing large blocks of hard and abrasive materials. Due to its robust structure and powerful crushing mechanism, it can handle materials with high hardness and abrasiveness, making it an essential equipment in many industrial applications.
All jaw crushers consist of two jaws: one is fixed, and the other is movable. The working principle is based on the reciprocating movement of the movable jaw. When the material enters the area between the two jaws, the movable jaw compresses and crushes the rock or ore against the fixed jaw. As the movable jaw moves back and forth relative to the fixed jaw, the material fed from the top of the machine is gradually compressed into smaller pieces. When the movable jaw moves away from the fixed jaw, the crushed material is discharged from the bottom of the crusher. The size of the discharged material is determined by the gap between the two jaws. This simple yet effective working principle ensures the efficient crushing of various materials.
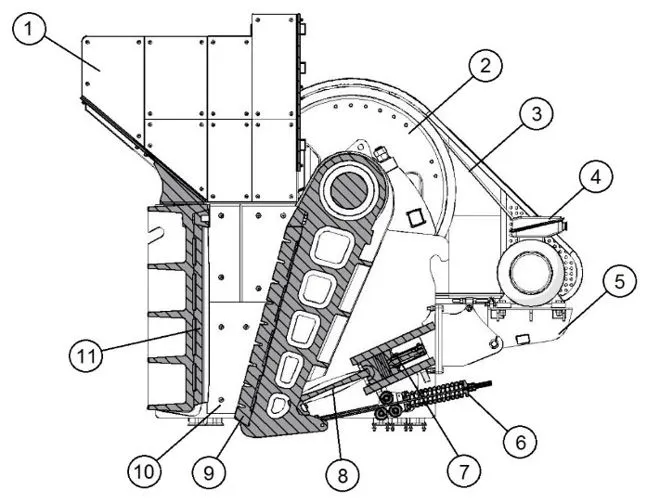
Feed Chute: It serves as the entry point for the materials to be crushed, guiding them smoothly into the crusher.
Drive Flywheel: It stores and releases energy during the crushing process, ensuring the stable operation of the crusher.
V - belts: These belts transfer the power from the electric motor to the drive flywheel, enabling the movement of the crusher components.
Electric Motor: The power source that drives the entire crusher, providing the necessary energy for the crushing operation.
Motor Stand: It supports the electric motor, ensuring its stability during operation.
Settings and Damping Group: This group is used to adjust the working parameters of the crusher and reduce vibrations during operation.
Hydraulic Cylinder: It can be used to adjust the gap between the jaws or for other operational adjustments, providing more flexibility in the crushing process.
Toggle Plate: It plays a crucial role in the movement of the movable jaw, transmitting the force and controlling the movement range.
Swing Jaw: The movable jaw that performs the actual crushing action by compressing the materials against the fixed jaw.
Discharge: The outlet through which the crushed materials are discharged from the crusher.
Fixed Jaw: The stationary jaw that provides the counter - force during the crushing process.
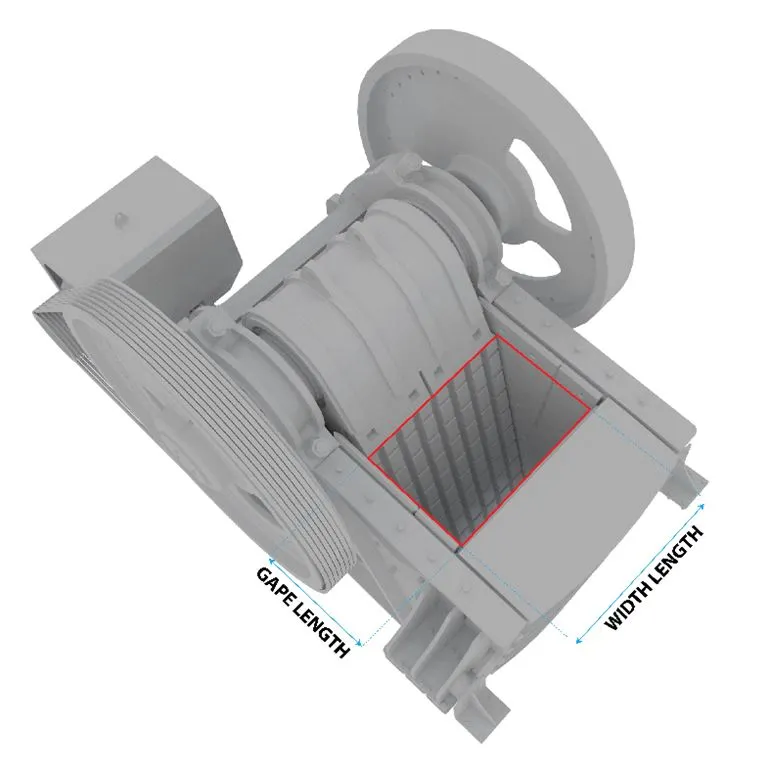
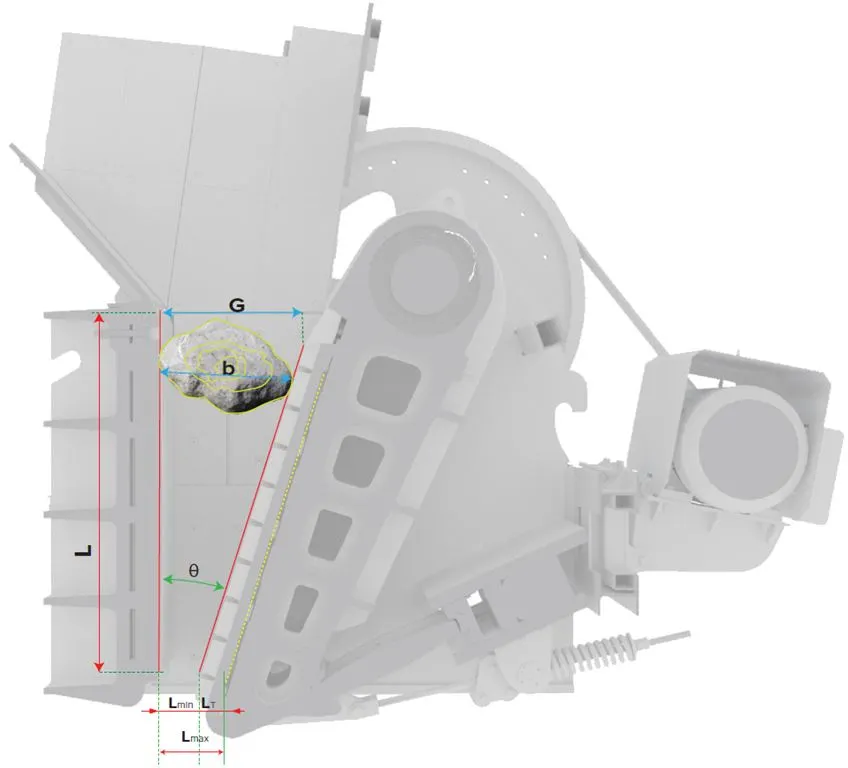
G (Gape width): This parameter determines the maximum feed size that the machine can handle. A larger gape width allows for the processing of larger - sized materials.
b (Maximum feed size): Generally, it is between 80% - 90% of the inlet width. This relationship ensures that the materials can be effectively fed into the crusher without causing blockages.
L (Area length): Approximately double the gape width. This length provides sufficient space for the materials to be crushed and processed.
W (Area width): Varies between 1.3 - 3 times the gape width. The width affects the capacity and efficiency of the crushing process.
Lmax (OSS, Open Side Setting) and Lmin (CSS, Closed Side Setting): These two parameters determine the range of the discharge size. By adjusting the OSS and CSS, the size of the crushed materials can be controlled according to the specific requirements.
Stroke (LT): The minimum and maximum movability of the lower end of the jaw, which is equal to OSS minus CSS. The stroke affects the crushing force and the efficiency of the crusher.
R (Size reduction ratio): The ratio of the gape width to the near - side jaw opening, generally ranging from 1/3 - 1/9. It is usually 1/3 for primary crushing and 1/4 for secondary crushing. This ratio reflects the degree of size reduction achieved by the crusher.
θ (Nip angle): The angle between the two jaws. It is one of the important parameters, depending on the size, hardness, and frangibility of the material. In primary crushing, it is generally between 18 - 24 degrees, and in secondary crushing, it is between 22 - 28 degrees, with a maximum of 33 degrees. The nip angle affects the gripping and crushing efficiency of the jaws on the materials.
Single - toggle Jaw Crushers: In a single - toggle jaw crusher, the movable jaw is supported by bearings on an eccentric shaft. This eccentric shaft is driven by a pitman, and the pitman is in turn supported by a toggle plate at the bottom of the movable jaw. Any point on the movable jaw moves in an elliptical orbit. During the operation, both pressure and friction forces are exerted on the materials to be crushed. This type of crusher is relatively common and is often used in the aggregate industry due to its cost - effectiveness and suitable performance for general - purpose crushing tasks.
Double - toggle Jaw Crushers: For double - toggle jaw crushers, the pitman is mounted on a fixed non - eccentric shaft located at the top of the crusher. There are two toggle plates, one on the left and one on the right, connected to the pitman. The left - hand toggle plate is linked to the jaw - supporting block, while the right - hand one is connected to the main body. This design enables the crusher to apply only pressure to the materials. Although double - toggle jaw crushers are more expensive than single - toggle ones, they have a longer lifecycle because no friction force is applied, which reduces wear and tear on components. They are typically used for crushing extremely hard and highly abrasive materials.
Materials are evenly fed into the crusher by a vibrating feeder. Once inside the crushing chamber, they are subjected to intense pressure between the fixed jaw and the movable jaw. The movable jaw, driven by a powerful motor and an eccentric shaft, oscillates back and forth. This oscillation exerts a strong squeezing force on the materials, breaking them into smaller pieces.
Chassis: It serves as the base of the entire machine, providing support and mobility. The chassis is designed to be sturdy enough to carry all the other components and withstand the vibrations and stresses during operation.
Jaws: Consisting of a fixed jaw and a movable jaw, they are the core components for crushing materials. The interaction between the two jaws creates the force required to break down the materials.
Vibrating Feeder: This component feeds the materials into the crusher in a controlled manner. It ensures a continuous and uniform flow of materials, preventing over - feeding or blockages in the crusher.
Conveyor Belt: After the materials are crushed, the conveyor belt transports them to different stages of the process, such as further processing or storage areas.
Power Unit: Usually an engine, it powers the crusher and all its auxiliary parts. The power unit provides the necessary energy to drive the movement of the jaws, the vibrating feeder, and the conveyor belt.
Tracks: The tracks enable the crusher to move across rough terrain and uneven surfaces. They provide stability and traction, allowing the mobile jaw crusher to be deployed in various locations.
Construction Sites: Mobile jaw crushers are highly useful on construction sites. During the demolition of old buildings, they can crush construction waste such as concrete and bricks into reusable aggregates. This not only reduces the amount of waste that needs to be transported to landfills but also provides valuable materials for new construction projects.
Quarries: In quarries, they are used to crush large rocks into smaller aggregates, which are then further processed into gravel, sand, and various grades of stone for construction purposes. The mobility of these crushers allows them to be moved around the quarry according to the location of the rock deposits.
Mining Operations: For mining operations, mobile jaw crushers are essential for the primary crushing of extracted ores. In gold mining, for example, large rocks containing gold ore are initially crushed to a smaller size, making subsequent processing steps such as grinding and extraction more efficient.
Recycling and Waste Management: They play a crucial role in recycling and waste management by reducing the size of various wastes, including metals, plastics, and glass. Smaller - sized waste materials are easier to handle and process further, facilitating the recycling process.
High Mobility: Mobile jaw crushers can be easily moved between different sites without the need for disassembly. This feature makes them extremely convenient for projects that require equipment to be relocated frequently.
Low Transportation Cost: Since they can operate directly at the material source, the need to transport raw materials over long distances is reduced. This significantly cuts down on transportation costs, which can be a major expense in many industries.
Versatility: They are suitable for a wide range of materials and applications, from hard rocks to recycled concrete. This versatility makes them a popular choice for various industries, including construction, mining, and recycling.
Easy Maintenance: The components of mobile jaw crushers are designed to be easily accessible. This allows for regular maintenance, repair, and replacement of worn - out parts, reducing downtime and ensuring the continuous operation of the crusher.
Energy - Saving and Environment - Friendly: With the use of advanced technologies and materials, modern mobile jaw crushers are designed to consume less energy during operation. They also produce fewer emissions, making them more environmentally friendly compared to older models.
Typically, mobile jaw crushers are more expensive to purchase than ordinary jaw crushers. This is because they integrate components such as a mobile chassis and a power unit. For example, the purchase price of an ordinary jaw crusher of a certain model is approximately 300,000 yuan, while the purchase price of a mobile jaw crusher of the same specification reaches 500,000 yuan, which is about 67% higher.
Energy Consumption: Mobile jaw crushers generally consume more energy because they need to power both the mobile device and the crusher itself. Suppose an ordinary jaw crusher consumes 50 kWh of electricity per hour, a mobile jaw crusher may consume 60 kWh per hour. However, in practical applications, considering that mobile jaw crushers can operate near the material source and reduce the energy consumption required for long - distance material transportation, the overall energy - consumption cost may be reduced.
Cost of Wear - part Replacement: The main wear - parts of both crushers are jaw plates, etc. Due to the same working principle, under the same crushing materials and working conditions, the wear rate and replacement cost of wear - parts are not very different. However, due to the more complex structure of mobile jaw crushers, the replacement difficulty of some wear - parts may be slightly higher, resulting in a slight increase in labor costs.
Ordinary jaw crushers have a relatively simple structure, which makes maintenance relatively easy and the maintenance cost low. On the other hand, although mobile jaw crushers are designed for easy maintenance, they have a higher overall maintenance cost. This is because they incorporate more mechanical and electrical components, such as the transmission system of the mobile chassis and the engine of the power unit. However, their high mobility can reduce the maintenance and debugging costs during equipment transfer.
In the long - term operation, mobile jaw crushers can significantly cut down transportation costs. For example, in a remote mining project with a long - distance material transportation, the annual transportation cost using an ordinary jaw crusher can reach up to 1 million yuan. But after using a mobile jaw crusher, the transportation cost is almost zero. After five years of operation, although the procurement cost and maintenance cost of the mobile jaw crusher are slightly higher, when considering the transportation cost comprehensively, the total cost is about 2 million yuan lower than that of the ordinary jaw crusher.
Intelligent Monitoring Systems: In the future, both types of crushers are likely to be equipped with intelligent monitoring systems. These systems use sensors to monitor the operating status of the equipment in real - time. For instance, temperature sensors can monitor the temperature of the bearings, vibration sensors can detect the vibration amplitude of the equipment, and current sensors can monitor the motor current. Once the parameters exceed the normal range, the system will automatically issue an alarm and adjust the equipment parameters according to the preset program. For example, when it is detected that the motor current is too high due to material blockage, the system will automatically reduce the feeding speed to avoid equipment failure.
Automatic Parameter Adjustment: The intelligent system can also automatically adjust the parameters of the crusher according to the material characteristics and production requirements. By analyzing the hardness and particle size of the incoming materials, it can automatically adjust the swing frequency and stroke of the jaw plates to optimize the crushing process, improve the crushing efficiency, and enhance the product quality.
New Wear - resistant Materials: In the manufacturing of crushers, new wear - resistant materials such as ceramic composites and high - performance alloys have broad application prospects. Ceramic composites have extremely high hardness and wear resistance. When used to make jaw plates, their wear resistance can be 2 - 3 times higher than that of traditional high - manganese steel. This greatly extends the service life of the jaw plates, reduces the number of replacements, and cuts down the maintenance cost.
New Corrosion - resistant Materials: For processing materials containing corrosive substances, new corrosion - resistant materials such as special stainless steels and acid - and - alkali - resistant polymer coatings can effectively protect the crusher components. For example, when processing ores containing acidic minerals, using crusher components coated with acid - and - alkali - resistant polymer coatings can significantly improve the corrosion resistance of the equipment, extend its service life, and enhance its performance.